Category: Software & IOT
Software design
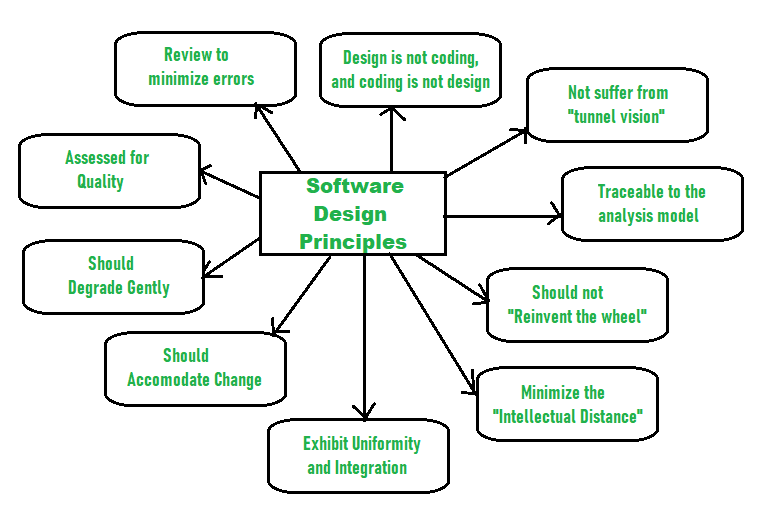
Software design is about the process of defining the architecture, components, interfaces, and other characteristics of a system or component. This is also called software architecture. Software design is divided into three different levels of design. The three levels are interface design, architectural design, and detailed design. Interface design is the interaction between a system and its environment. This happens at a high level of abstraction along with the inner workings of the system. Architectural design has to do with the major components of a system and their responsibilities, properties, interfaces, and their relationships and interactions that occur between them. Detailed design is the internal elements of all the major system components, their properties, relationships, processing, and usually their algorithms and the data structures.
Software construction
Software construction, the main activity of software development, is the combination of programming, unit testing, integration testing, and debugging. Testing during this phase is generally performed by the programmer while the software is under construction, to verify what was just written and decide when the code is ready to be sent to the next step.
Software testing
Software testing is an empirical, technical investigation conducted to provide stakeholders with information about the quality of the product or service under test, with different approaches such as unit testing and integration testing. It is one aspect of software quality. As a separate phase in software development, it is typically performed by quality assurance staff or a developer other than the one who wrote the code.
Software maintenance
Software maintenance refers to the activities required to provide cost-effective support after shipping the software product. Software maintenance is modifying and updating software applications after distribution to correct faults and to improve their performance. The software has a lot to do with the real world and when the real world changes, software maintenance is required. Software maintenance includes error correction, optimization, deletion of unused and discarded features, and enhancement of features that already exist. Usually, maintenance takes up about 40% to 80% of the project cost therefore, focusing on maintenance keeps the costs down.
.-
 A software Design and implementation
A software Design and implementation
Design and implementation...
Read more -
 Software engineering degree programs
Software engineering degree programs
Half of all practitioners...
Read more -
 Definitions and terminology controversies
Definitions and terminology controversies
Margaret Hamilton promote...
Read more -
 History about software
History about software
Beginning in the 1960s, s...
Read more -
 IOT Military applications
IOT Military applications
The Internet of Military...
Read more